
- #SOLUTION CHEMISTRY CALCULATOR PDF#
- #SOLUTION CHEMISTRY CALCULATOR PLUS#
- #SOLUTION CHEMISTRY CALCULATOR FREE#
The substances are separated by a plus sign (+). Reactants and products in a chemical reaction are separated by an equal sign (=).The method is modified for finding integer coefficients. Our stoichiometry calculator uses the Gauss-Jordan elimination algorithm for solving a set of linear equations. But in case of complex reactions involving many compounds, it is preferable to balance equations using algebraic methods, based on solving a set of linear equations. There are a number of methods for balancing chemical equations. In case of ionic reactions, the same electric charge must be present on both sides of the equation. Thus, each side of the equation must represent the same quantity of atoms of any chemical element. It’s important because in a chemical reaction, the quantity of each element does not change (the law of conservation of mass). This means looking for stoichiometric coefficients for the reactants and products. So, the first step in stoichiometry calculations is balancing chemical equations. Knowing the molecular weight of the compounds involved in the reaction, it is easy to find the mass of these compounds in grams. For any balanced chemical equation, whole numbers (stoichiometric coefficients) are used to show the amounts (in moles) of both the reactants and products.

Stoichiometry is the field of chemistry that studies the relative amounts of reactants and products in chemical reactions. You can enter either the required number of moles or weight in grams for one of the compounds in the corresponding field, and then press the ‘Enter’ key, to compute new values for the rest of the compounds. The reaction stoichiometry is calculated automatically for a balanced equation, with the number of moles for the compounds being the same as the stoichiometric coefficients. In what follows is a more detailed syntax guide to our calculator.
#SOLUTION CHEMISTRY CALCULATOR PDF#
You can enter a chemical equation manually or paste the equation copied from a web page or text document (including DOC or PDF file). In case the original equation was unbalanced, the field with this equation is highlighted in light pink.
#SOLUTION CHEMISTRY CALCULATOR FREE#
The equations may include free electrons and electrically charged molecules (ions) as well as hydrated compounds. Have a glance at the online calculator tools from Chemistrycalc.Com & enhance your chemistry skills and understand the concepts easily.This online Stoichiometry Calculator finds the stoichiometric coefficients to balance a given chemical equation and computes amounts of the reactants and products of the reaction, both in moles and grams.

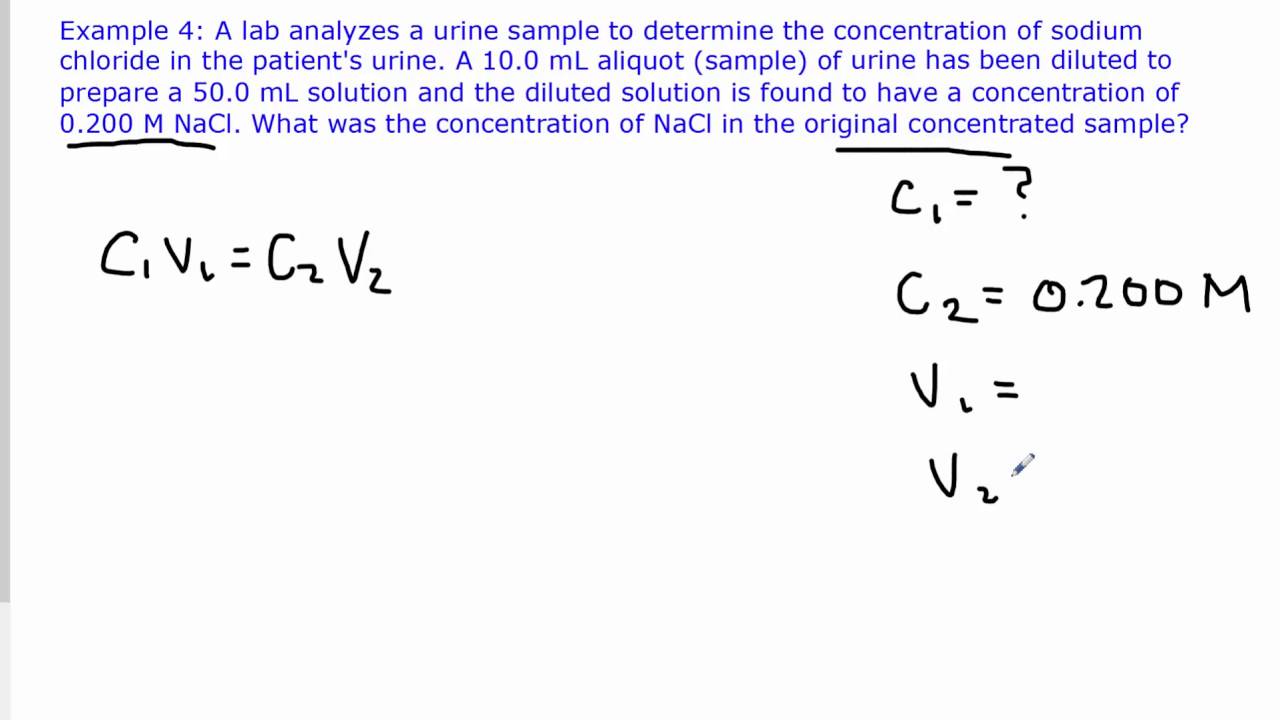
Molarity = number of moles of solute/volume of solution The number of moles of sodium sulphate in the given question is calculated as, The molecular weight of sodium sulphate = 142 The volume of the solution = 125 ml = 0.125 litres Calculate the molarity of the given solution of sodium sulphate. Question: A solution was prepared using 15 g of sodium sulphate. It depends on the changes in physical properties of the system and is represented as M. The molarity of a solution is defined as the total number of moles of solute per litre of solution. Mole is the SI unit for the measurement of the amount of substance. If a mole is used, the elementary entities should be specified and may be atoms, molecules, electrons, and other particles. The mole is the amount of substance of a system that has as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 0.12 kgs of carbon-12.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
